Apikit 产品实操白皮书
免费下载
Apikit 产品路线图
立即跳转
Apikit 产品立项材料
立即申请
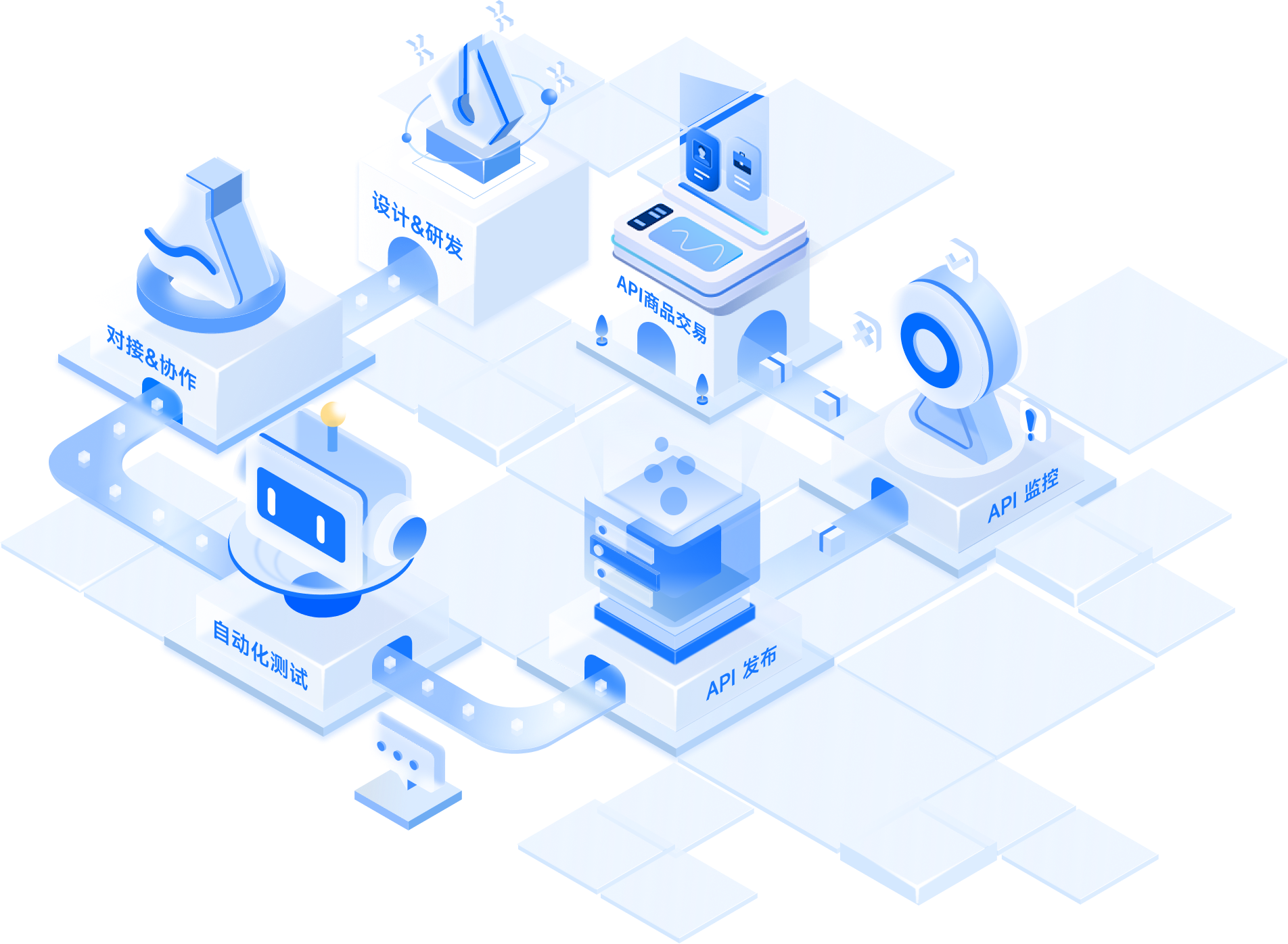
团队开发者的 API
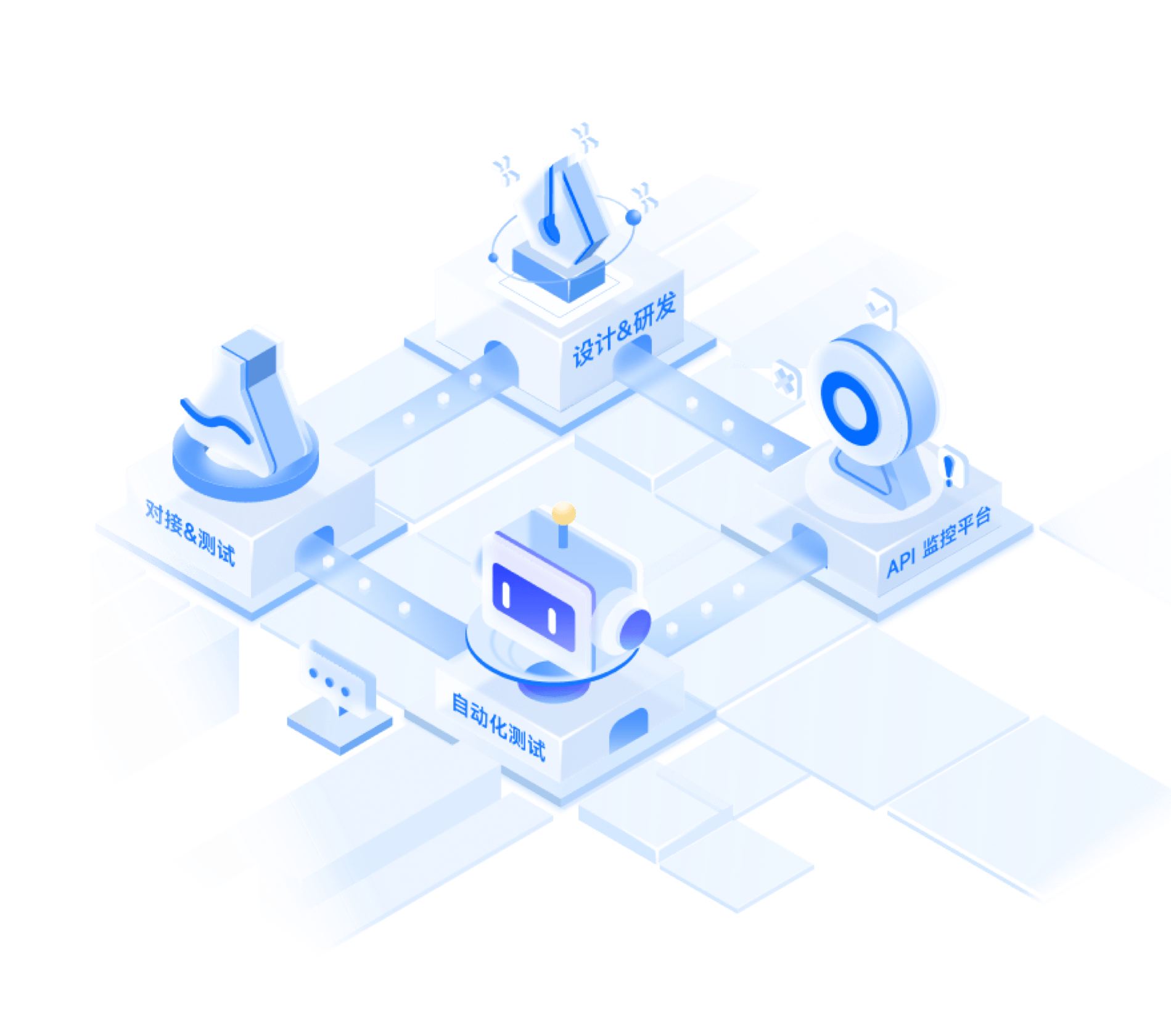
全生命周期工作流
设计 & 研发
强大易用的 API 文档管理
工具效率提高 60%!
对接 & 测试
实时接收变更通知,快速在线协作
评论和调试API
自动化测试
首创零代码自动化测试,降低
95% 测试时间
API 发布
超高性能,比 Nginx、Kong 等产品快约 50%!
API 监控
7*24 小时秒级监控
保障API资产安全
API 商品交易
100万开发者提供服务
年均100亿次接口调用,稳定可靠
通过开源积极促进 API 生态的发展
XPack 是全球首个开源 MCP 交易平台。将任何OpenAPI转换为可变现的MCP服务,10分钟内构建您自己的MCP 交易平台。
XPack 是开源软件,采用Apache 2.0许可证。可自由用于个人和商业项目。
Postcat 是集成 API 管理、测试、Mock、团队协作的轻量级 API 开发协作工具,可以取代 Swagger + Postman + Mock等工具,并具有强大的插件系统,可以自由扩展功能。
Apinto 网关是用 GO 语言模块化开发的微服务网关。它支持集群和动态扩容应用管理,以及精细化流量的服务治理,能够满足企业级"开箱即用"的需求。此外,提供了丰富的网关插件和企业插件,也支持企业自定义插件来解决企业的定制化需求。

APIPark 是开源企业级 API 开放平台,你能通过 APIPark 快速在企业内部构建 API 开放门户/市场,享受极致的转发性能、API可观测、服务治理、多租户管理、订阅审批流程等诸多好处。
Eolink API 商店
全场商品免费试用,为百万开发者提供专业的 API 服务,深圳数据交易所、贵阳大数据交易所 官方合作伙伴XRoute 提供统一的大语言模型接口。一次充值,全球大模型任意调用。无需逐一开户,无需受调用限制困扰。✨ 现已支持调用 GPT-5 ✨
DeepSeek-R1DeepSeek R1(深度推理)是一款高性能大语言模型API,具备强大的自然语言理解与生成能力,适用于各类文本处理任务。无论是智能问答、内容创作、代码生成,还是数据分析与摘要提取,DeepSeek R1 都能提供精准、高效的响应,助力企业快速构建智能化应用。
DeepSeek-V3DeepSeek-V3 API 是一款基于先进人工智能技术的接口服务,具备强大的自然语言理解与生成能力。它支持 128K 超长上下文,能够高效处理复杂对话、长文档分析及多轮交互任务,并在中文场景下进行了深度优化。通过简洁的 API 接口,开发者可轻松集成 DeepSeek-V3 到客服系统、内容创作工具或数据分析平台中,享受其高效、精准的 AI 能力。
实名认证 身份证二要素核验身份证二要素(姓名和身份证号码)信息是否一致。 直连官方权威渠道,精准实时核验,99.99%准确率。
天气预报查询支持全国以及全球多个城市的天气查询,包含国内3400+个城市以及国际4万个城市的实况数据,同时也支持全球任意经纬度查询,接口会返回该经纬度最近的站点信息;更新频率分钟级别。
IP归属地-IPv4区县级根据IP地址查询归属地信息,包含43亿全量IPv4,支持到中国地区(不含港台地区)区县级别,含运营商数据。
手机号码归属地手机号码归属地,提供全国移动、联通、电信等手机号码归属地查询,上亿条数据囊括最新的170、166、147等号段,更新及时、准确度高
空气质量查询支持国内3400+个城市的整点观测,并附带空气质量监测点(全国共2335个)的整点观测数据;支持国内经纬度查询,返回最近的站点信息。获取指定城市的整点观测空气质量,包含空气质量指数(AQI)、首要污染物、空气质量等级(优、良、轻度污染、中度污染、重度污染、严重污染)、6要素(CO、NO₂、O₃、PM10、PM2.5、SO₂)浓度(除了CO浓度单位为mg/m³之外,其余5种单位均为μg/m³)等。
全国快递物流查询1.提供包括申通、顺丰、圆通、韵达、中通、汇通等100+快递公司在内的快递物流单号查询。2.与官网实时同步更新。3.根据单号自动识别快递公司,识别单号不收费。
空号检测通过手机号码查询其在网活跃度,返回包括空号、实号、停机、库无、沉默号、风险号等状态。
深受众多行业领先企业信任
Eolink 相信 API 能帮助全球企业充分发挥数据和服务的价值,作为国内最早的 API 全生命周期管理理念的推动者
陆续为各行业超过10万企业管理数亿 API,覆盖互联网、汽车、能源、金融、房地产、企业服务、信息安全、酒店旅游、游戏文娱等多个行业
陆续为各行业超过10万企业管理数亿 API,覆盖互联网、汽车、能源、金融、房地产、企业服务、信息安全、酒店旅游、游戏文娱等多个行业
来自权威机构的认证

高新技术企业

可信云

等保三级认证

信创产品认证

鲲鹏认证

ISO 27001质量认证

ITSS 工具认证

ISO 9001质量认证

深圳数据交易所

贵阳大数据交易所

TARS 成员认证

linux 成员认证

NextArch 成员

麒麟软件认证